Difference between revisions of "Authorization Code flow description"
Pavel.lobko (talk | contribs) |
Pavel.lobko (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[File:Bridge flow scheme.png|600px]] | [[File:Bridge flow scheme.png|600px]] | ||
| + | The flow illustrated in Figure 3 includes the following steps: | ||
| + | |||
| + | (A) The client initiates the flow by directing the resource owner's | ||
| + | user-agent to the authorization endpoint. The client includes | ||
| + | its client identifier, requested scope, local state, and a | ||
| + | redirection URI to which the authorization server will send the | ||
| + | user-agent back once access is granted (or denied). | ||
| + | |||
| + | (B) The authorization server authenticates the resource owner (via | ||
| + | the user-agent) and establishes whether the resource owner | ||
| + | grants or denies the client's access request. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (C) Assuming the resource owner grants access, the authorization | ||
| + | server redirects the user-agent back to the client using the | ||
| + | redirection URI provided earlier (in the request or during | ||
| + | client registration). The redirection URI includes an | ||
| + | authorization code and any local state provided by the client | ||
| + | earlier. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (D) The client requests an access token from the authorization | ||
| + | server's token endpoint by including the authorization code | ||
| + | received in the previous step. When making the request, the | ||
| + | client authenticates with the authorization server. The client | ||
| + | includes the redirection URI used to obtain the authorization | ||
| + | code for verification. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (E) The authorization server authenticates the client, validates the | ||
| + | authorization code, and ensures that the redirection URI | ||
| + | received matches the URI used to redirect the client in | ||
| + | step (C). If valid, the authorization server responds back with | ||
| + | an access token and, optionally, a refresh token. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
[[I2Rest_Client|Back to i2Rest Client]] | [[I2Rest_Client|Back to i2Rest Client]] | ||
Revision as of 14:42, 22 May 2020
The authorization code grant type is used to obtain both access
tokens and refresh tokens and is optimized for confidential clients.
Since this is a redirection-based flow, the client must be capable of
interacting with the resource owner's user-agent (typically a web
browser) and capable of receiving incoming requests (via redirection)
from the authorization server.
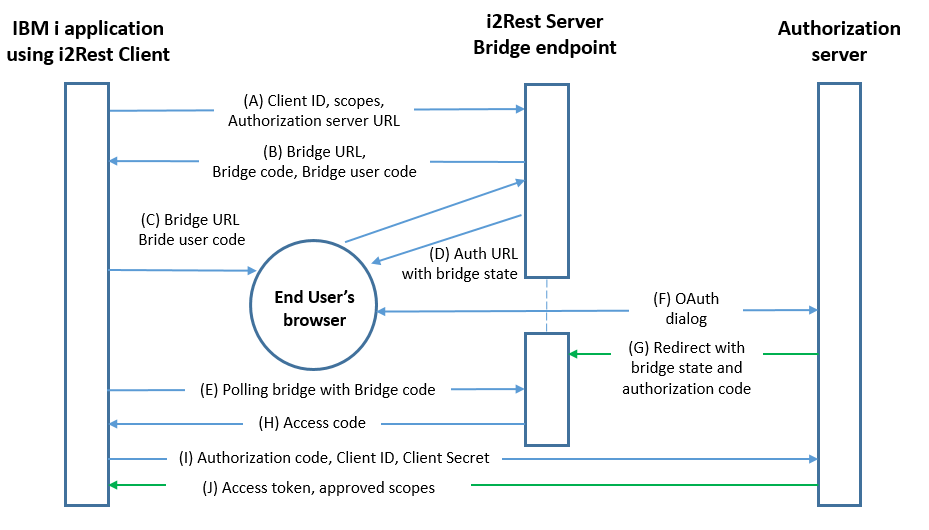
The flow illustrated in Figure 3 includes the following steps:
(A) The client initiates the flow by directing the resource owner's
user-agent to the authorization endpoint. The client includes
its client identifier, requested scope, local state, and a
redirection URI to which the authorization server will send the
user-agent back once access is granted (or denied).
(B) The authorization server authenticates the resource owner (via
the user-agent) and establishes whether the resource owner
grants or denies the client's access request.
(C) Assuming the resource owner grants access, the authorization
server redirects the user-agent back to the client using the
redirection URI provided earlier (in the request or during
client registration). The redirection URI includes an
authorization code and any local state provided by the client
earlier.
(D) The client requests an access token from the authorization
server's token endpoint by including the authorization code
received in the previous step. When making the request, the
client authenticates with the authorization server. The client
includes the redirection URI used to obtain the authorization
code for verification.
(E) The authorization server authenticates the client, validates the
authorization code, and ensures that the redirection URI
received matches the URI used to redirect the client in
step (C). If valid, the authorization server responds back with
an access token and, optionally, a refresh token.