Difference between revisions of "Authorization Code flow description"
Pavel.lobko (talk | contribs) |
Pavel.lobko (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Authorization Code flow using i2Rest bridge mode description}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Authorization Code flow using i2Rest bridge mode description}} | ||
| − | Authorization Code flow using i2Rest bridge has not too much diferencies from [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749#section-4.1 original Authorization Code flow] - we just have to implement two "bridges" to solve IBM i functional limitations. So here | + | Authorization Code flow using i2Rest bridge has not too much diferencies from [https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749#section-4.1 original Authorization Code flow] - we just have to implement two "bridges" to solve IBM i functional limitations. So here are our limitations and solutions: |
- i2Rest Client is not capable of interacting with the resource owner's user-agent (typically a web browser), this functions are delegated to the i2Rest Server. To perform the delegation i2Rest Client have to provide i2Rest Server with all the necessery request details and bring the end user's agent to Bridge endpoint. This process is described in steps A-B-C.<br> | - i2Rest Client is not capable of interacting with the resource owner's user-agent (typically a web browser), this functions are delegated to the i2Rest Server. To perform the delegation i2Rest Client have to provide i2Rest Server with all the necessery request details and bring the end user's agent to Bridge endpoint. This process is described in steps A-B-C.<br> | ||
Revision as of 15:39, 27 May 2020
Authorization Code flow using i2Rest bridge has not too much diferencies from original Authorization Code flow - we just have to implement two "bridges" to solve IBM i functional limitations. So here are our limitations and solutions:
- i2Rest Client is not capable of interacting with the resource owner's user-agent (typically a web browser), this functions are delegated to the i2Rest Server. To perform the delegation i2Rest Client have to provide i2Rest Server with all the necessery request details and bring the end user's agent to Bridge endpoint. This process is described in steps A-B-C.
- i2Rest Client also is not capable of receiving incoming requests via redirection, so I2Rest Server have to receive Authorization Server redirection with access code attached. Then obtained access code should be linked to initial Client communication, and returned to the Client uppon request. The process is described in steps G-E-H.
Lets take a look on scheme.
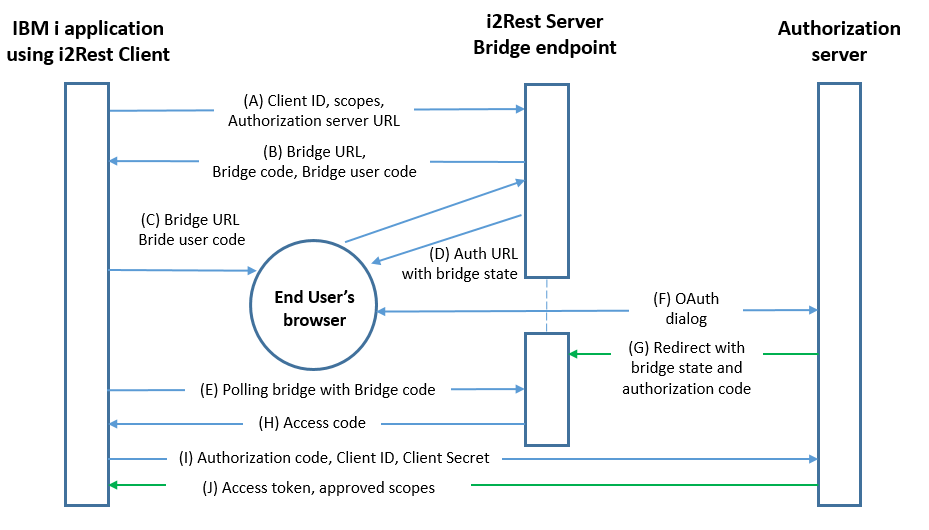
(А) i2Rest Client initiates the flow with a request to the I2Rest Server Bridge endpoint. The request incudes client identifier, requested scope and Authorization Server URL (authorization endpoint).
(B) I2Rest Server responds with Brigde URL, Bridge User Code and Bridge Code.
(C) i2Rest Client instructs the user to visit provided Brigde URL using device with input capability and browser support.
(D) i2Rest Server directs the resource owner's user-agent to the authorization endpoint. Request contains i2Rest Client identifier, requested scope, Bridge local state, redirection Bridge URI to which the authorization server will send the user-agent back once access is granted (or denied).
(E) i2Rest Client starts polling I2Rest Server bridge with Bridge code to determine whether the user has authorized the request.
(F) The authorization server authenticates the resource owner (via the user-agent) and establishes whether the resource owner grants or denies access request.
(G) The authorization server redirects the user-agent back to the i2Rest Server using the redirection URI provided earlier (in the request or during client registration). The redirection URI includes an authorization code and Bridge local state provided earlier.
(H) i2Rest Server bridge responds with authorization code if access was granted or with an error if access was denied.
(I) i2Rest Client requests an access token from the authorization server's token endpoint by including the authorization code received in the previous step. When making the request, the client authenticates with the authorization server. The client includes the redirection URI used to obtain the authorization code for verification.
(J) The authorization server authenticates the client, validates the authorization code, and ensures that the redirection URI received matches the URI used to redirect the client in step (C). If valid, the authorization server responds back with an access token and, optionally, a refresh token.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Authentication method | *OAUTH2C must be specified
|
| Command | Any of available request type can be choosen |
| API endpoint | HTTP resource to serve the request |
| Tokens storage | ??????? |
| User/OAuth2 client/device ID | Client Credentials to authenticate with authorization server |
| User/OAuth2 client/dev passwd | |
| OAuth2 token endpoint | HTTP resource used by the client to abtain an access token |
| Scope | the set of resources and operations that are allowed to application with access token |