Difference between revisions of "I2Camunda"
(→Anonymous calls) |
(→Anonymous calls) |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
Source: [https://www.i2rest.com/download/i2Camunda_samples/Simple_I2RESTECHO.bpmn https://www.i2rest.com/download/i2Camunda_samples/Simple_I2RESTECHO.bpmn]<br/> | Source: [https://www.i2rest.com/download/i2Camunda_samples/Simple_I2RESTECHO.bpmn https://www.i2rest.com/download/i2Camunda_samples/Simple_I2RESTECHO.bpmn]<br/> | ||
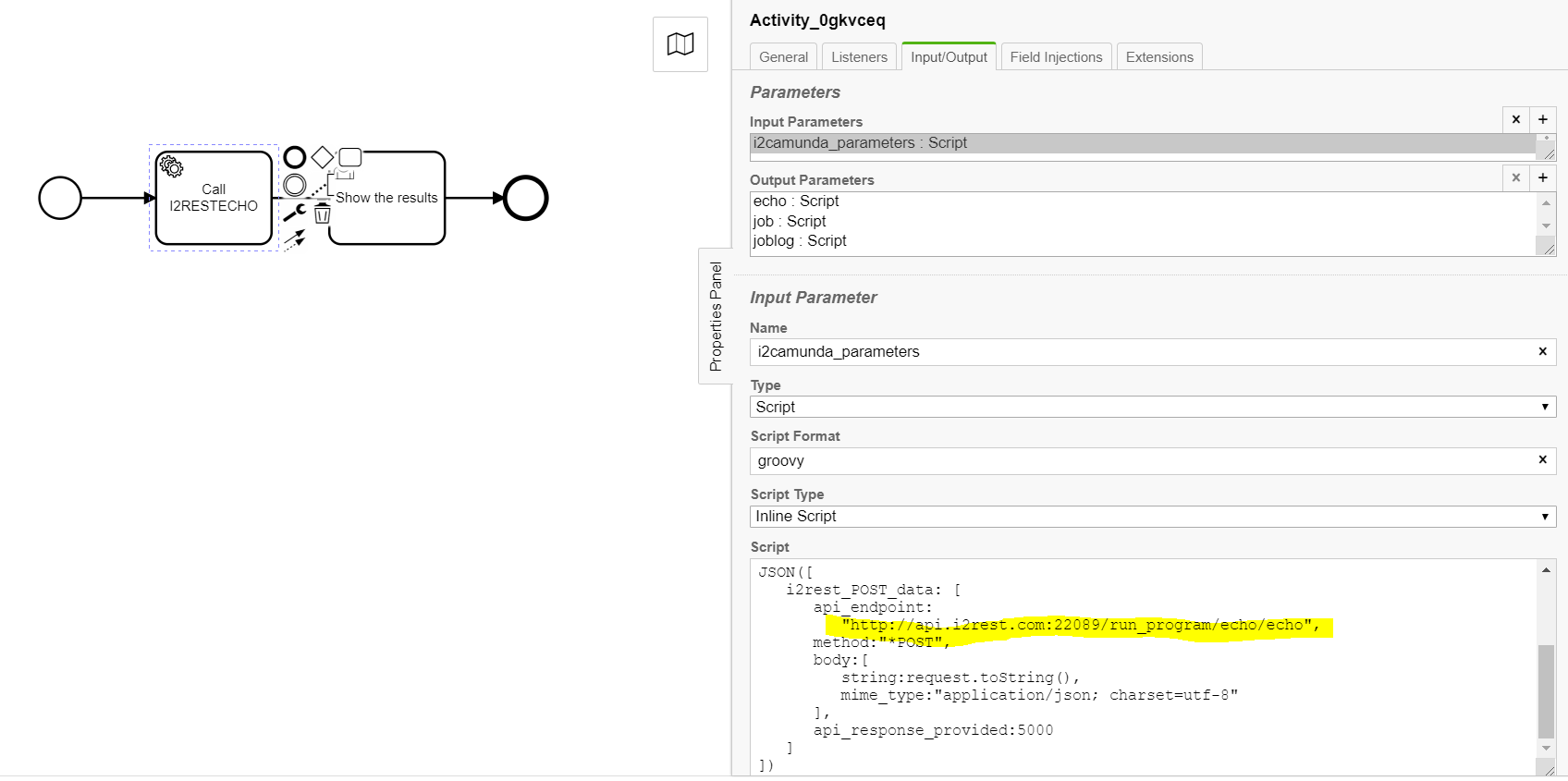
Do not forget to enter actual URL of your i2Rest Server instance at the i2camunda_parameters input mapping:<br/> | Do not forget to enter actual URL of your i2Rest Server instance at the i2camunda_parameters input mapping:<br/> | ||
| − | [[File:Simple I2RESTECHO i2camunda parameters.PNG| | + | [[File:Simple I2RESTECHO i2camunda parameters.PNG|700px]]<br/> |
Revision as of 15:15, 4 August 2020
We are still working on this topic. Please contact contacts@i2rest.com if you would like to get information asap
i2Camunda is a separate extension for i2Rest Server, which is designed to organize the interaction of the Camunda BPM engine with IBM i programs and commands via i2Rest Server APIs.
Contents
What is Camunda
Camunda is currently one of the most prominent players in the business process automation industry. From wikipedia:
- Camunda BPM is an open-source workflow and decision automation platform. Camunda BPM ships with tools for creating workflow and decision models, operating deployed models in production, and allowing users to execute workflow tasks assigned to them. It is developed in Java and released as open-source software under the terms of Apache License.
- It provides a Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) standard compliant workflow engine and a Decision Model and Notation (DMN) standard compliant decision engine, which can be embedded in Java applications and with other languages via REST.[1]
More details can be found at the Camunda's official site
i2Camunda as an External Task processor for Camunda
The concept of external tasks is well described on the Camunda official documentation website: https://docs.camunda.org/manual/latest/user-guide/process-engine/external-tasks/
i2Camunda plays the role of the External worker in this concept. i2Camunda is a batch job on IBM i, which subscribes to specific topic(s) and consume calls to REST APIs of i2Rest Server:
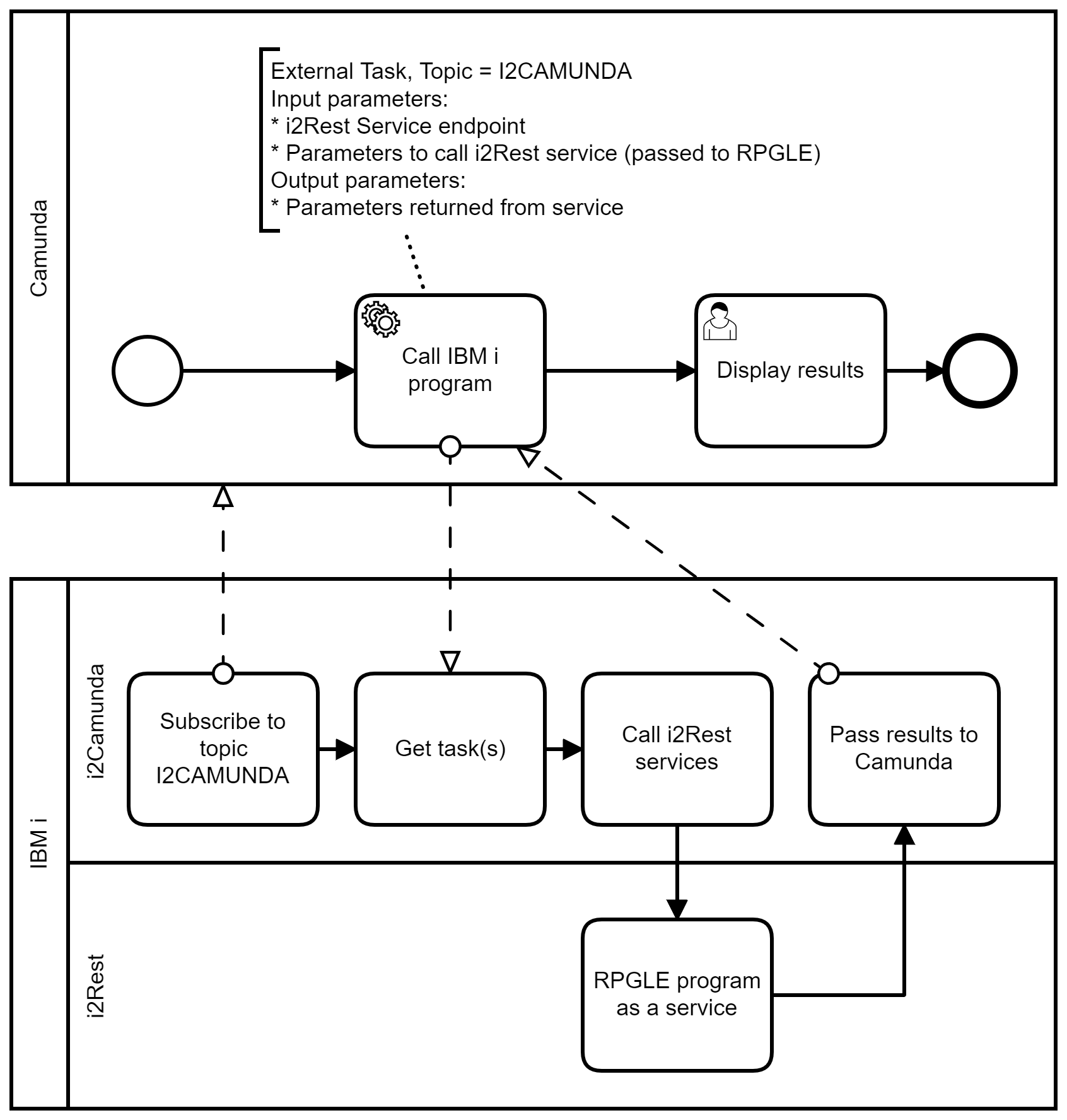
This diagram shows communications on the simplest BPMN process. The upper part displays the business process configured and executed in the Camunda environment, the lower part shows the interaction of i2Rest and i2Camunda, that works natively on IBM i platform
- After submitting, i2Camunda subscribes to Camunda as an external worker that will process external tasks with "I2CAMUNDA" topic
- When some Camunda's business process will reach external task with such topic, i2Camunda will get peace of job to work
- i2Camunda will call i2Rest Service in accordance with external task parameters defined in the BPMN diagram
- Output parameters of RPGLE program will be passed to Camunda as a process variables, and task will be marked as Completed
i2Camunda input parameters
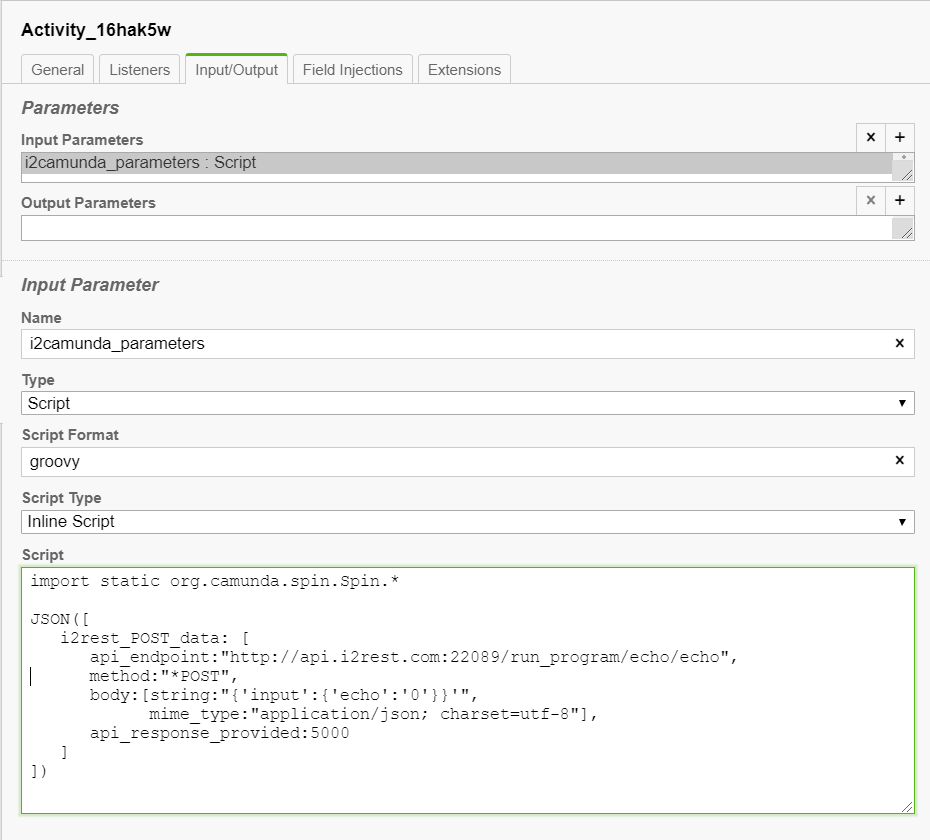
In order to pass parameters to i2Camunda, it is required to define external task's Input parameter:
Task's input parameter "i2camunda_parameters" has to contain all data required to call REST API. It can contain one of the following objects, depending on the function that is required to call:
- i2rest_POST_data - to make simple http request to web server, with or without OAuth2 access token
- i2rest_request_authorize - to request user and device codes (first step of OAuth2 Device code flow)
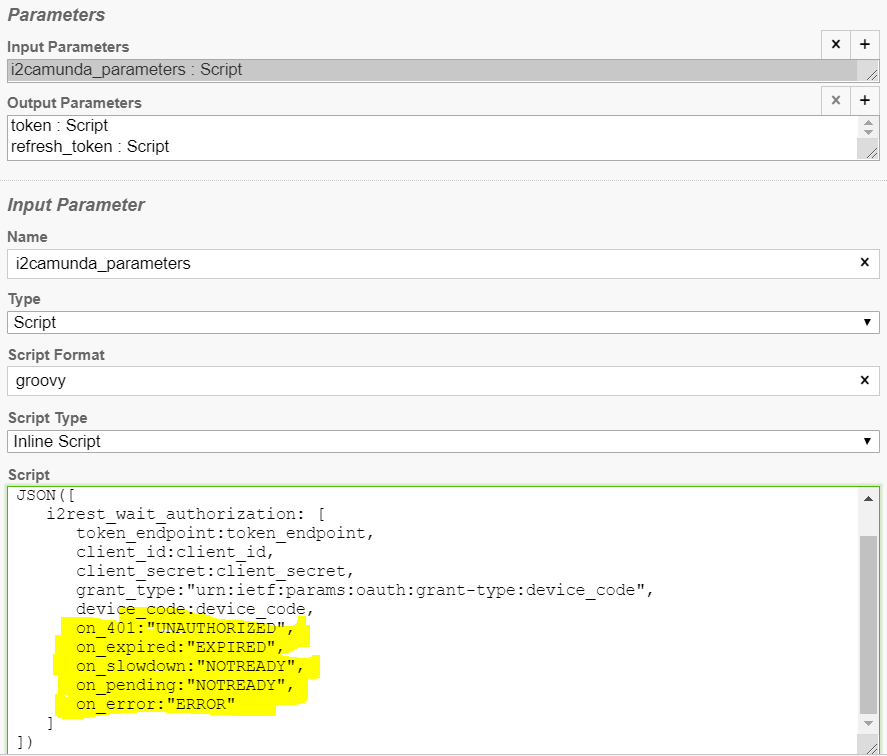
- i2rest_wait_authorization - to get OAuth2 token (last step of OAuth2 Device code flow)
- i2rest_get_fresh_token - to present refresh token and exchange it to new access token (OAuth2 Refresh token flow)
- i2rest_request_client_credentials_token - to obtain OAuth2 Client credentials token
- i2rest_request_bridge_authorize - to submit the request for Access code (first step of OAuth2 Access code flow in i2Rest Bridge mode)
- i2rest_get_access_token - to get Access code (second step of OAuth2 Access code flow in i2Rest Bridge mode)
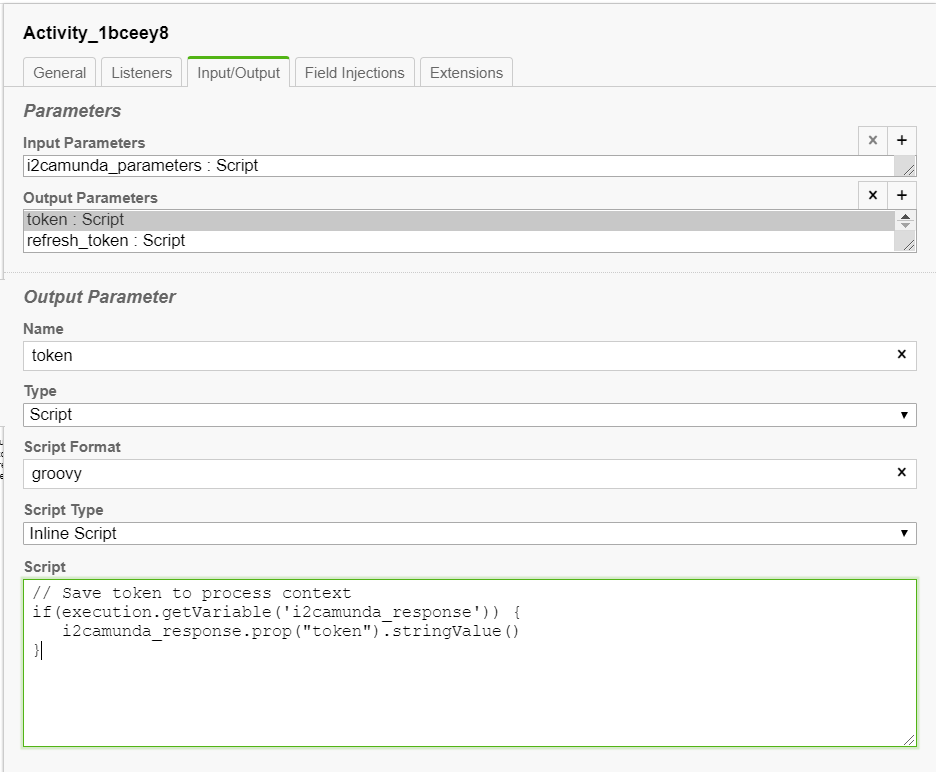
i2Camunda output parameters
When the call to i2Rest service ends, i2Camunda completes task and sets local variable named i2camunda_response. You can use this variable in the Output mapping to retrieve response data and set required process variables, for example:
The type of local variable i2camunda_response is SpinJsonNode. To access its properties, it is required to use method prop, like shown above. More details here: https://docs.camunda.org/manual/latest/reference/spin/json/01-reading-json/#reading-json-properties
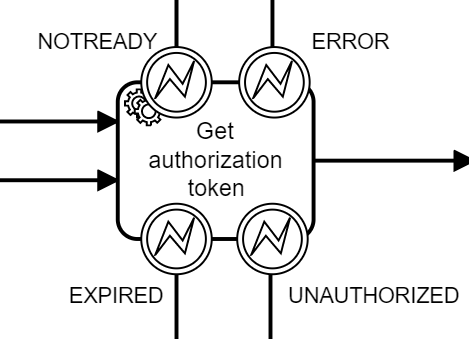
Handling i2Camunda BPMN errors
Like any other service, calls to i2Rest Server APIs can return errors. Errors can be vary - from authorization errors to functional errors returned by RPGLE programs. Depending on parameters, defined in i2camunda_parameters, i2Camunda can raise BPMN errors, or create incidents. Each i2Camunda function has set of predefined parameters where you can define the codes for BPMN error to raise. In case of errors, the task will be completed with a corresponding BPMN error. If no corresponding BPMN error is defined for an error, or if an BPMN error cannot be raised, an incident will be created.
For example:
and a piece of BPMN diagram:
How to install i2Camunda
See i2Camunda installation instructions
i2Camunda configuration
To run i2Camunda you must prepare configuration file. Configuration file is a text file stored on IFS system. It has to contain i2Camunda settings object in JSON format - see i2Camunda configuration object
How to start i2Camunda instance
To start i2Camunda instance, please add I2REST library to your library list, and issue the following command:
SBMJOB CMD(CALL PGM(I2CAMUNDA) PARM('-start' '-config' '<path to i2Camunda configuration file>')) ALWMLTTHD(*YES)
You can set up other parameters of SBMJOB according your requirements. It it required to set ALWMLTTHD(*YES)
Sample processes
All sample processes shown here uses I2RESTECHO program to demonstrate program calls
Anonymous calls
This case was built on top of basic i2Rest setup
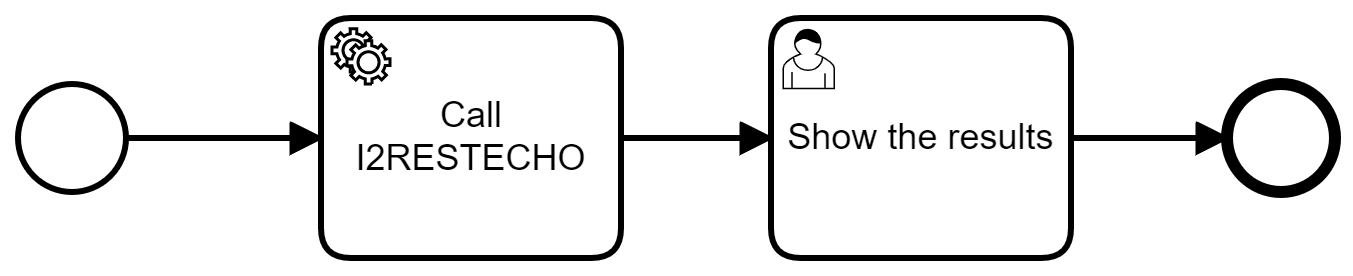
Source: https://www.i2rest.com/download/i2Camunda_samples/Simple_I2RESTECHO.bpmn
Do not forget to enter actual URL of your i2Rest Server instance at the i2camunda_parameters input mapping: